
Easily transition to retirement with the right strategy. Learn how it works — and how an advisor can help you retire with confidence.
Written by:
Joel Simmonds
Head of Advice
Debt recycling might sound complicated, but it’s actually a straightforward strategy that can help you use your home loan to build wealth.
In simple terms, debt recycling in Australia means turning non-tax-deductible debt, like your mortgage, into tax-deductible debt that you can claim on your tax return. By doing this, you can start investing, pay off your home loan quicker, and potentially save on tax.
Read on as we explain how you can use debt recycling to your advantage.
Debt recycling works by taking equity from your home loan and investing it in income-producing assets like shares or an investment property.
You then use the income from those investments to pay off your mortgage faster. Over time, your home loan shrinks, and you’re left with tax-deductible debt on your investments.
To give an example of debt recycling, let’s say you’ve paid off a good chunk of your mortgage and have built up $200,000 in equity. You can borrow against that equity to buy shares or invest in property. The interest on this loan is tax-deductible, and the returns from the investment help you pay off your home loan quicker.
Imagine Peter and Michelle, a couple who’ve been paying off their mortgage for several years. They’ve built $300,000 of equity in their home.
They decide to use debt recycling by borrowing $150,000 from their home loan to buy shares. The interest on the loan is tax-deductible, and they use the dividends and tax savings to pay down their mortgage faster.
Over time, they’ve turned their non-tax-deductible home loan into an investment loan that offers tax benefits.
When incorporated into a well-structured financial plan, debt recycling can help reduce the costs of holding investments.
Some of the benefits include:
Debt recycling can be particularly beneficial if you have a solid income and a long-term investment mindset.
Like any financial strategy, there are pros and cons of debt recycling.
The main risk is that you’re borrowing more, which could become difficult to manage if interest rates rise or your investments underperform.
You’re also reliant on maintaining steady income to cover both your home loan and the debt recycling loan structure.
One of the key benefits of debt recycling is that the interest on an investment loan is tax-deductible.
However, it’s important to understand that claiming the interest doesn’t result in a 100% refund. Instead, the amount you save depends on your marginal tax rate.
For example, if you’re in the 37% tax bracket and claim $10,000 in interest, you would save $3,700 in taxes (37% of the interest amount). This means you reduce your taxable income, but you won’t receive the full interest amount back.
Debt recycling can be an effective strategy for those looking to pay off their home faster while building wealth through investments.
Debt recycling is a strategy designed to help individuals pay off their home faster while growing their investment portfolio. In this example, we’ll look at how debt recycling could work in a scenario where the individual has a salary of $180,000 and a $750,000 mortgage. Over a 10-year period, this example shows how the strategy may lead to potential long-term financial benefits.
Without Debt Recycling:
With Debt Recycling (at 5.99% interest):
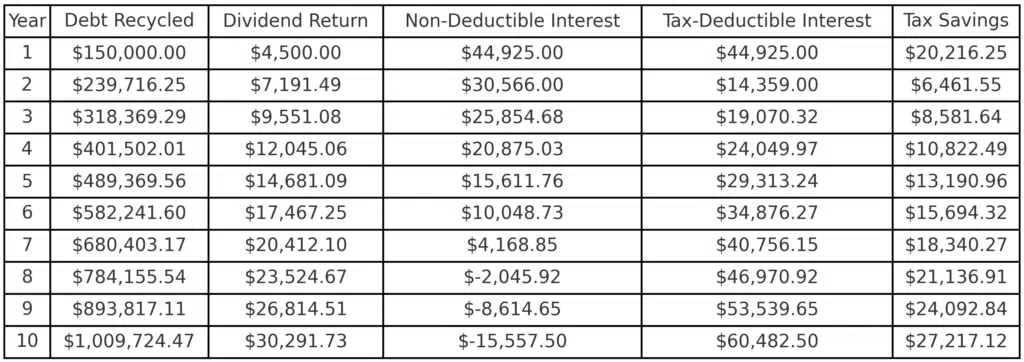
By implementing a debt recycling strategy at an interest rate of 5.99%, this example demonstrates how significant financial benefits might be realised over a 10-year period. The strategy could result in total tax savings of $165,754.35 through the conversion of home loan debt into tax-deductible investment debt.
Additionally, potential interest savings of $125,831.99 could be achieved by using investment income and tax savings to pay down the non-deductible mortgage faster.
In total, the example shows an overall benefit of $291,586.34, illustrating how debt recycling can be an effective tool to reduce costs and build wealth more efficiently over time.
When you split your home loan for the purposes of debt recycling, the interest is calculated separately for each portion of the loan.
The total interest you’ll pay remains comparable to what you would pay if you hadn’t split the loan. Here’s how it works:
First Loan Portion (Owner-Occupied Loan): This is the portion of your loan tied to your home (such as the 20% deposit). The interest on this portion remains non-deductible because it relates to your primary residence.
Second Loan Portion (Investment Loan): This is the amount you’ve split off for investment purposes. The interest on this portion is tax-deductible because it’s used for an income-generating investment.
The interest for each portion of the loan is calculated independently based on the balance and interest rate.
No, using debt recycling doesn’t mean you’ll pay more interest.
The total interest across both loans would be comparable to what you’d pay if you kept the loan whole, but with an added tax benefit on the investment portion.
The key difference is that splitting the loan allows you to make the interest on the investment portion tax-deductible, potentially reducing your overall tax liability.
Debt recycling works best when you’re borrowing money to invest in new income-generating assets.
However, if you already own investments, you generally cannot use debt recycling to retroactively make the interest on these investments tax-deductible. Here’s why:
In some cases, you could sell the investment and repurchase it using borrowed funds, but this may trigger capital gains tax and other costs. It’s important to seek professional advice before considering this option.
While debt recycling seems like a cheat code to help you build wealth, it’s actually just a smart strategy that is perfectly legal in Australia.
The ATO allows you to claim interest on investment loans, as long as the borrowed money is used to generate income, such as rent or dividends.
Make sure to check your loan and investment details to ensure they meet ATO guidelines.
If you’re keen to explore this strategy, here’s a debt recycling step-by-step process:
You can use a debt recycling calculator to figure out how much equity you can tap into and what kind of returns you might expect from your investments.
Debt recycling calculators available in Australia can also help you determine how quickly you’ll be able to pay off your home loan with this strategy.
You might be wondering about debt recycling vs offset accounts. While both can help you pay off your home loan faster, debt recycling offers the added benefit of tax deductions.
An offset account helps reduce your interest but doesn’t come with the tax perks that debt recycling offers. However, if you prefer a simpler option, offset accounts can be easier to manage.
Another comparison to consider is debt recycling vs negative gearing. Negative gearing allows you to claim losses on your investment properties, while debt recycling turns your home loan into an investment loan that offers tax benefits.
Both can work well in Australia, but debt recycling gives you the added benefit of paying off your home loan faster.
If you have stable income, a long-term investment mindset, and are comfortable with risk, debt recycling can be a powerful way to build wealth.
However, it’s not for everyone. Is debt recycling worth it? That depends on your goals and whether you’re prepared for the risks involved.
We’re here to help you navigate this decision and ensure that debt recycling fits your financial plan. Reach out to our team for expert advice tailored to your situation—together, we can make sure you’re on the right path to achieving your goals.
Erin provides insights into our investment advice services, explaining how we help you build a tailored investment strategy.
Discover how we align your investments with your financial goals, ensuring a balanced approach that enables growth while carefully managing risk.
Here’s some of the most commonly asked questions about debt recycling and using it as an investment tool.
If your questions isn’t answered below, then please feel free to get in touch. We’re always happy to help.
Debt recycling in Australia is a financial strategy that turns non-deductible debt (such as a home loan) into tax-deductible debt by borrowing against your home equity and investing in income-producing assets like shares or property.
To set up debt recycling, you’ll need to build equity in your home first. From there, you can borrow against that equity to invest in assets. It’s crucial to consult a financial advisor and ensure your loan structure supports debt recycling.
Make sure you can manage the repayments on both the home loan and the new investment loan.
A debt recycling spreadsheet is a tool used to track the details of your debt recycling strategy. It helps you calculate how much equity you can borrow, what your repayments will be, and how your investments are performing over time.
Many people use spreadsheets to stay on top of their progress and ensure they are meeting their financial goals.
Split loan debt recycling refers to dividing your mortgage into two parts: one that covers your home loan and one for the loan used to invest. The split allows you to better manage repayments while keeping track of what portion of your debt is tax-deductible and what isn’t.
Yes, debt recycling can be used to buy shares. When you borrow against your home equity to invest in shares, the interest on that loan becomes tax-deductible.
The income you earn from dividends can then be used to pay off your home loan faster.
Yes, you can use debt recycling to purchase an investment property. The loan for the investment property is tax-deductible, and any rental income you receive can go toward paying off your home loan more quickly.
This allows you to build wealth while also shrinking your non-deductible debt.
A debt recycling offset account is simply a regular offset account that’s linked to your home loan. It functions like any other offset account by reducing the interest you pay on your home loan.
The difference is that, when combined with a debt recycling strategy, you can use it more effectively.
While you’re investing borrowed equity into income-producing assets, the money in your offset account works to lower the interest on your non-deductible home loan, helping you pay it off faster.
Yes, you can use debt recycling with interest-only loans. This can be an effective strategy as you only pay the interest on your investment loan while focusing on paying off the principal of your home loan.
However, it’s important to manage your cash flow carefully and consult a financial advisor to ensure this setup works for your financial situation.
Read More

Easily transition to retirement with the right strategy. Learn how it works — and how an advisor can help you retire with confidence.

Super contributions can help you grow your retirement savings faster and save tax — but the rules, caps and strategies can be tricky. Here’s what you need to know to get it right in 2025.

Property vs Shares in Australia (2025): Which Investment Strategy Fits You?

Wondering if investing in property is still smart in 2025? We break down the risks, returns, insights, and expert advice to help you decide.

Planning for retirement doesn’t have to feel overwhelming. This guide walks you through how much super you might need to retire comfortably in Australia, how to work it out by age, and what income you can expect in retirement.

Wondering if a financial advisor is worth the cost? Learn how expert advice can help grow wealth, minimise tax, and keep you on track for retirement.
This is a publication of Direct Wealth Pty Ltd, a wholly owned subsidiary of Direct Wealth Group Pty Ltd.
General Advice Warning – The information contained in this article is of a general nature and does not take into account your particular objectives, financial situation or needs. You should therefore consider the appropriateness of the advice for your situation before acting on it. You should obtain and consider the relevant Product Disclosure Statement (PDS) and seek the assistance of an authorised financial adviser before making any decisions regarding any products or strategies mentioned in this publication.
Disclaimer – While all care has been taken in the preparation of this blog, to the maximum extent permitted by law, no warranty is given in respect of the information provided and accordingly, neither Direct Wealth nor its related bodies corporate, employees or agents shall be liable for any loss suffered arising from reliance on this information.